

Introducing Rustemo: A LR/GLR Parser Generator for Rust
Igor Dejanović (igord at uns ac rs), University of Novi Sad
Agenda

1. Introduction
1.1. Introduction
- An old-school LALR(1) parser generator (a.k.a. compiler-compiler) … with a modern twist - context aware lexing, GLR, flexible lexers/builders.
- Project started in November 2021
- Bootstrapping done in August 2022
- Generalized LR - Elizabeth Scott, Adrian Johnstone, Right Nulled GLR Parsers, 2006.
- Name: serbian word “растемо” pronounced as “rustemo” means “we grow”
1.2. Rustemo compiler
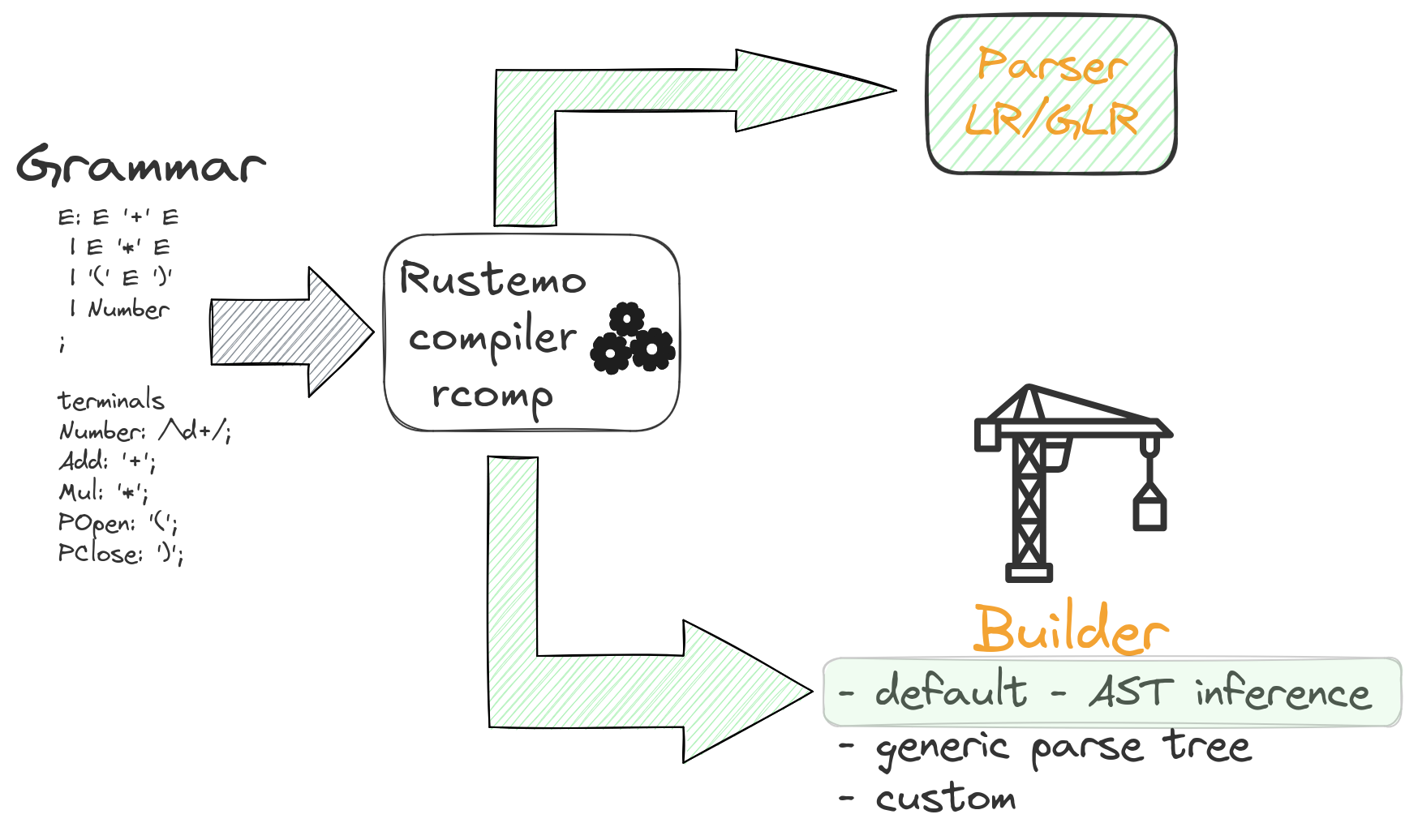
1.3. Rustemo compiler
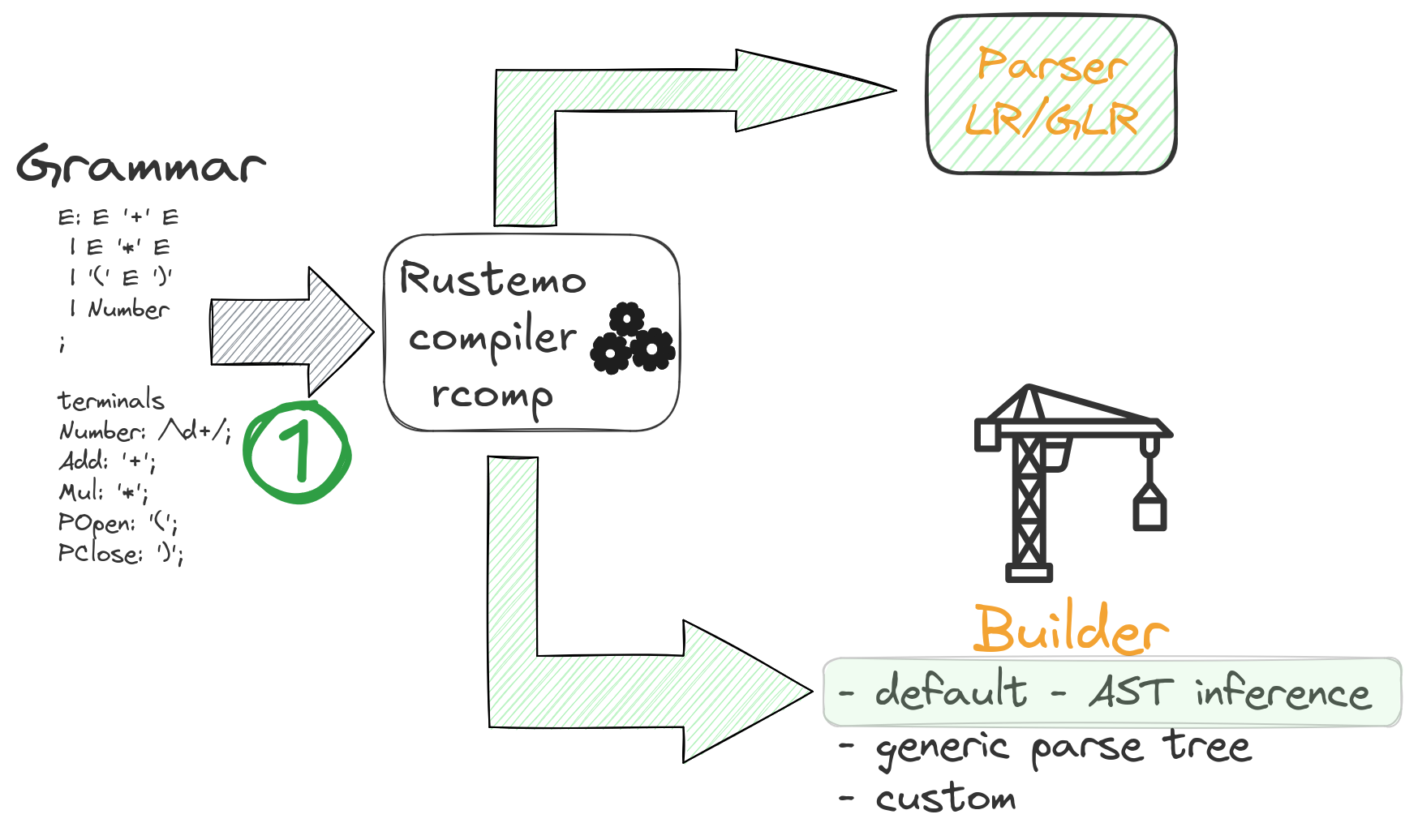
1.4. Rustemo compiler
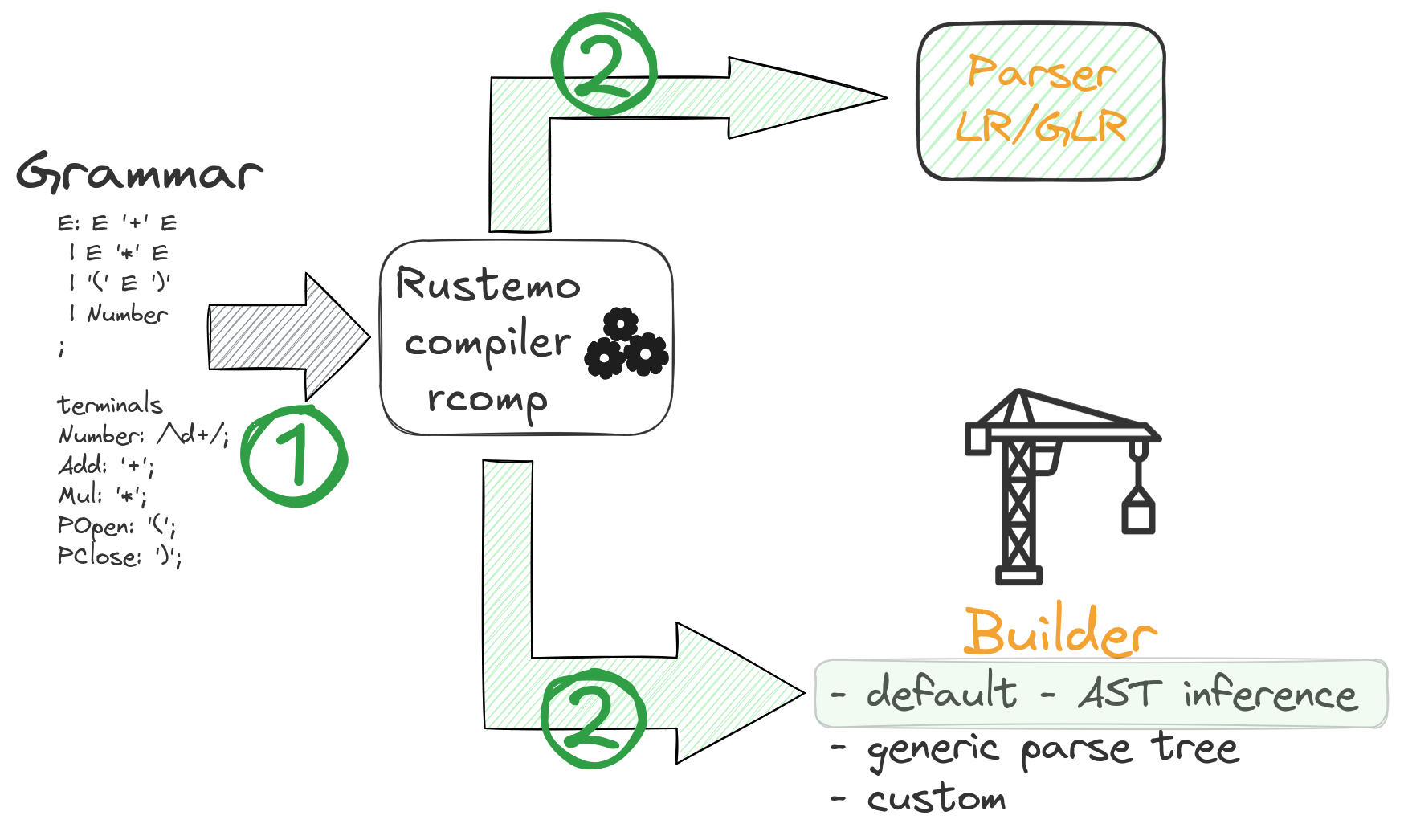
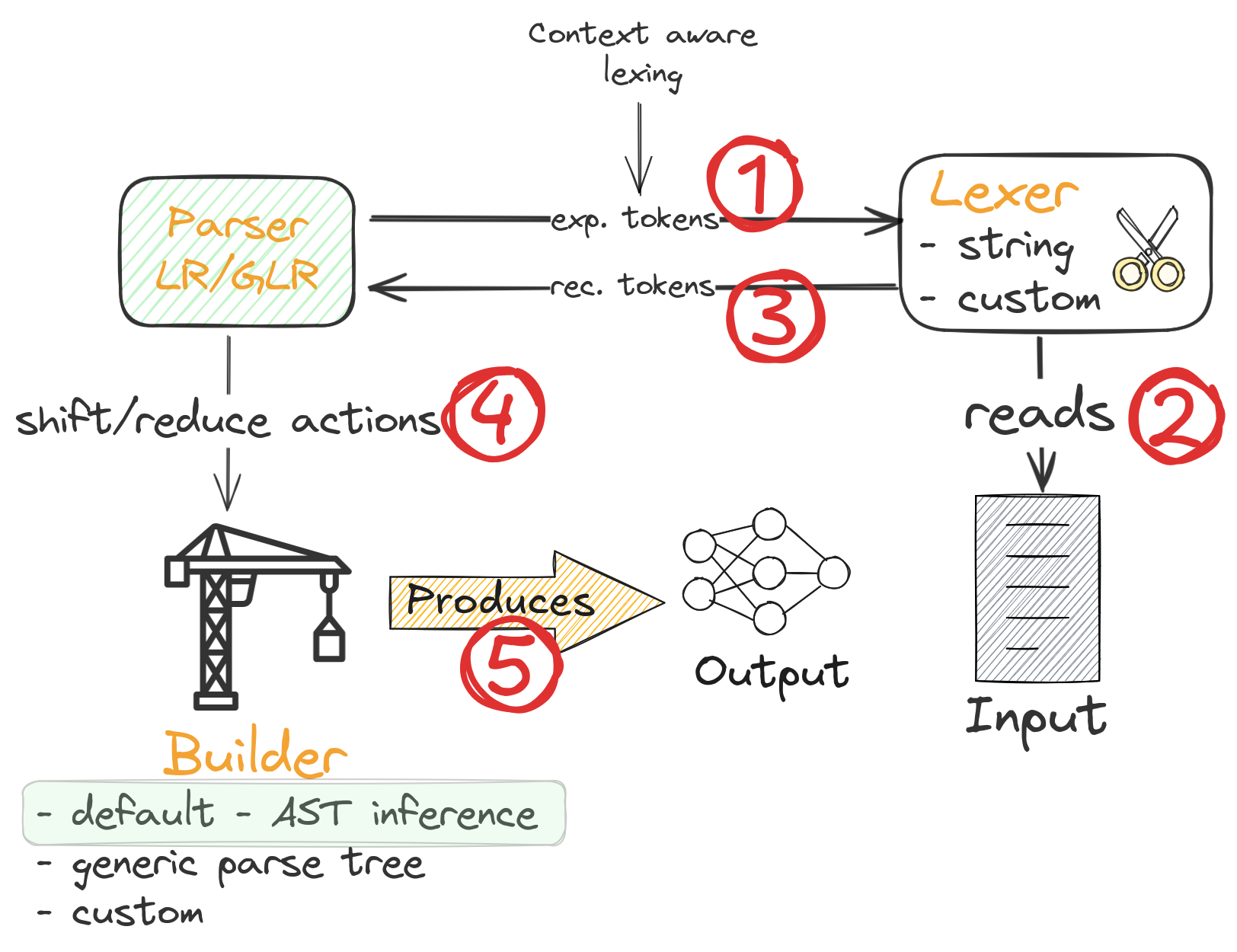
1.5. Parsing process overview
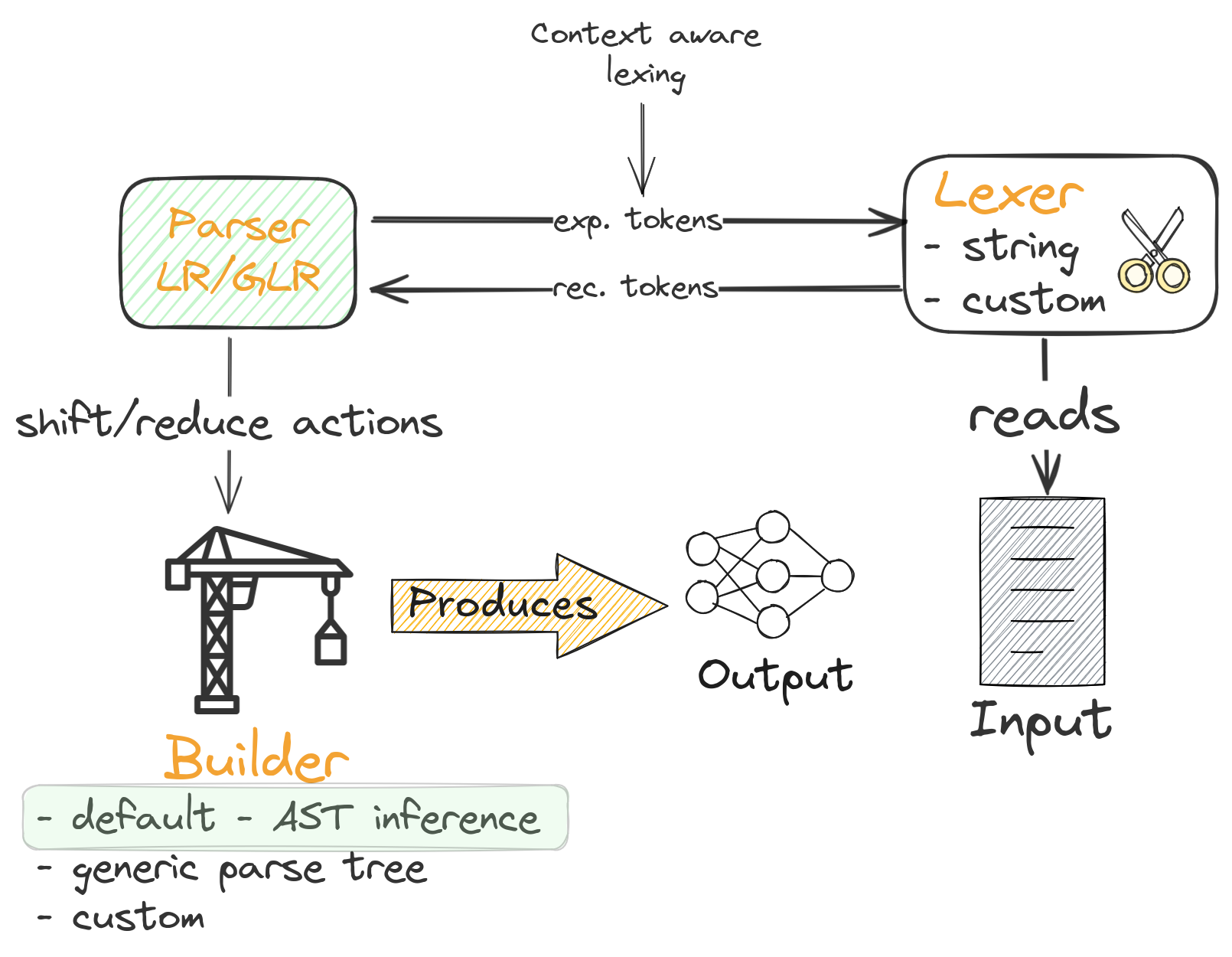
1.6. Parsing process overview
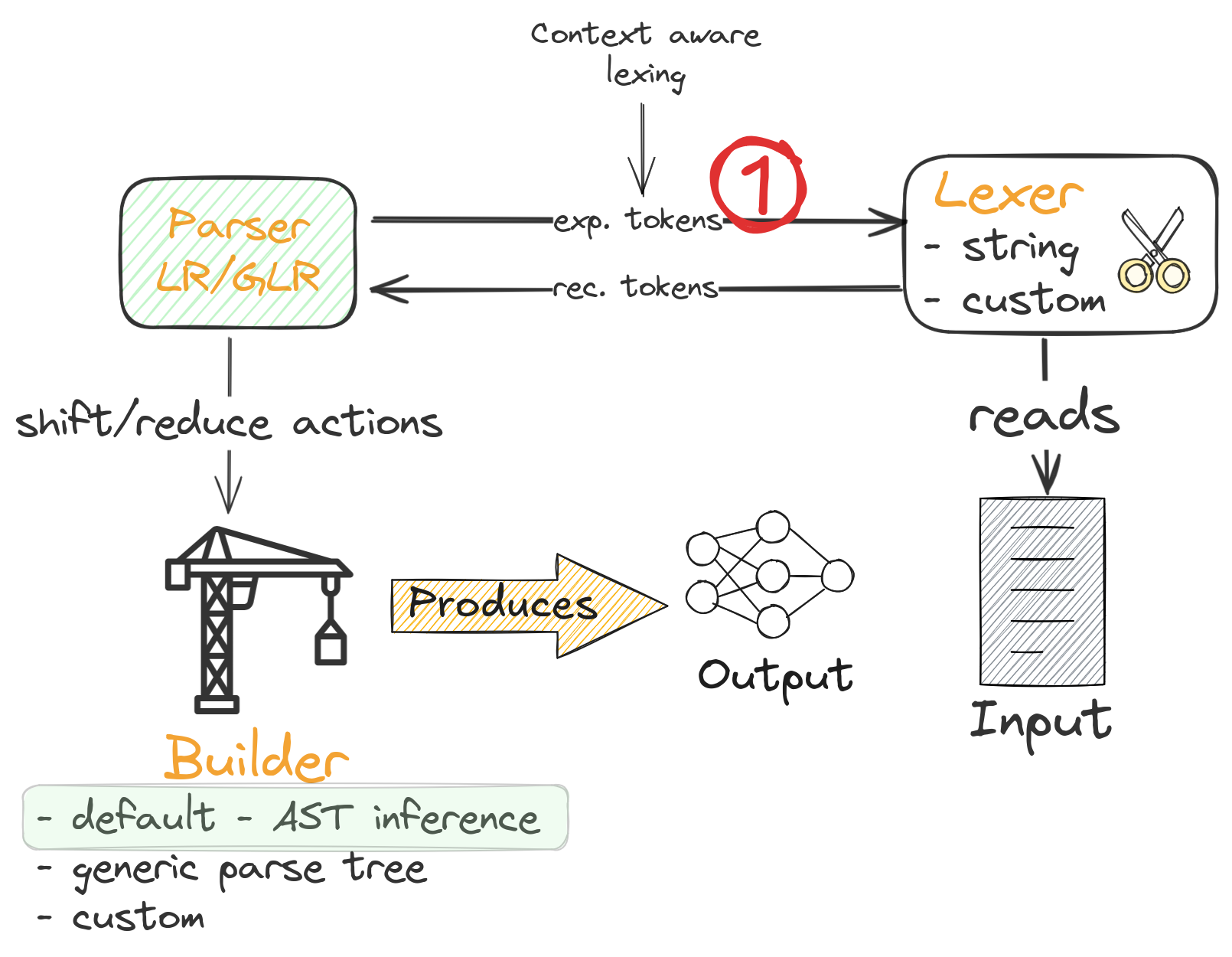
1.7. Parsing process overview
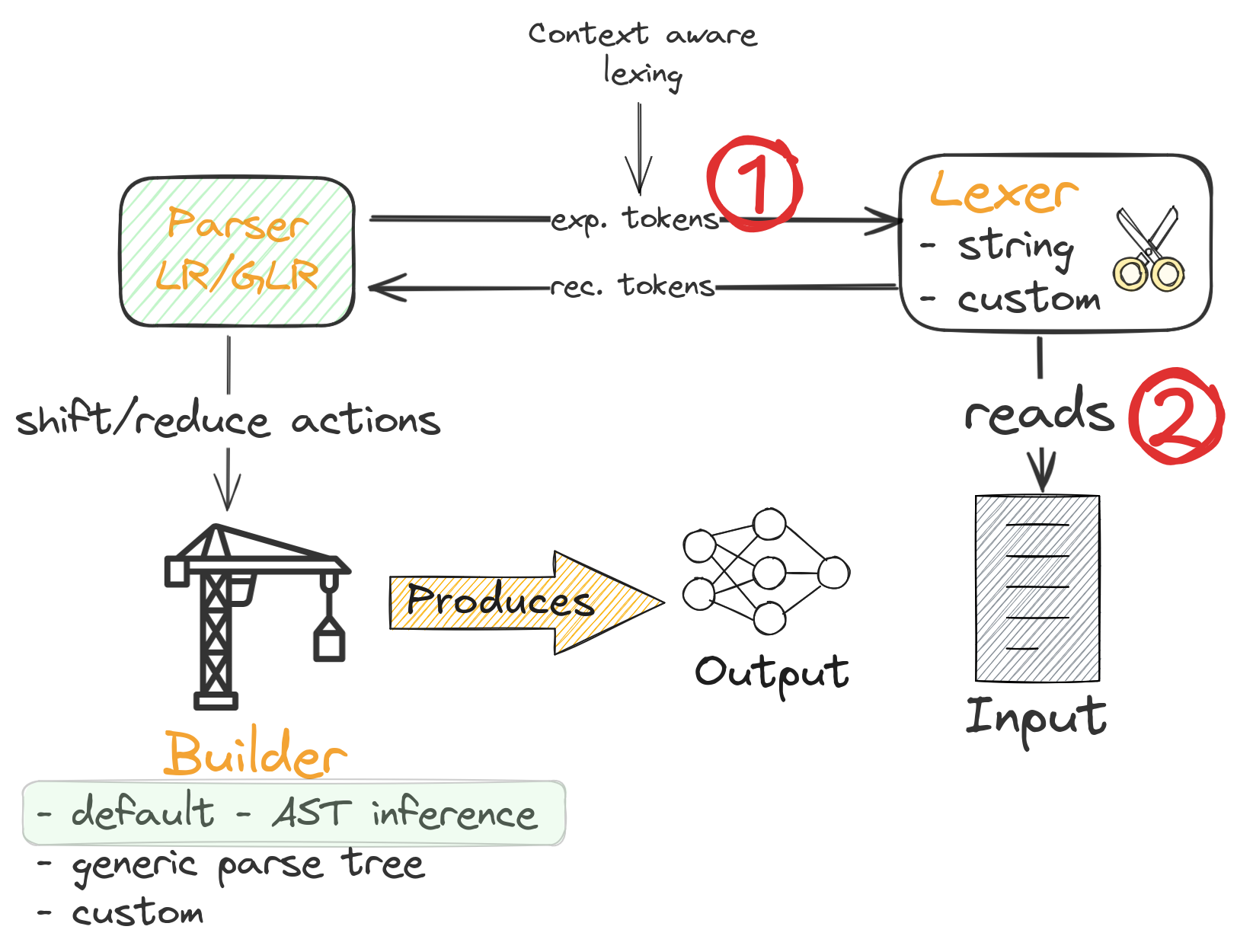
1.8. Parsing process overview
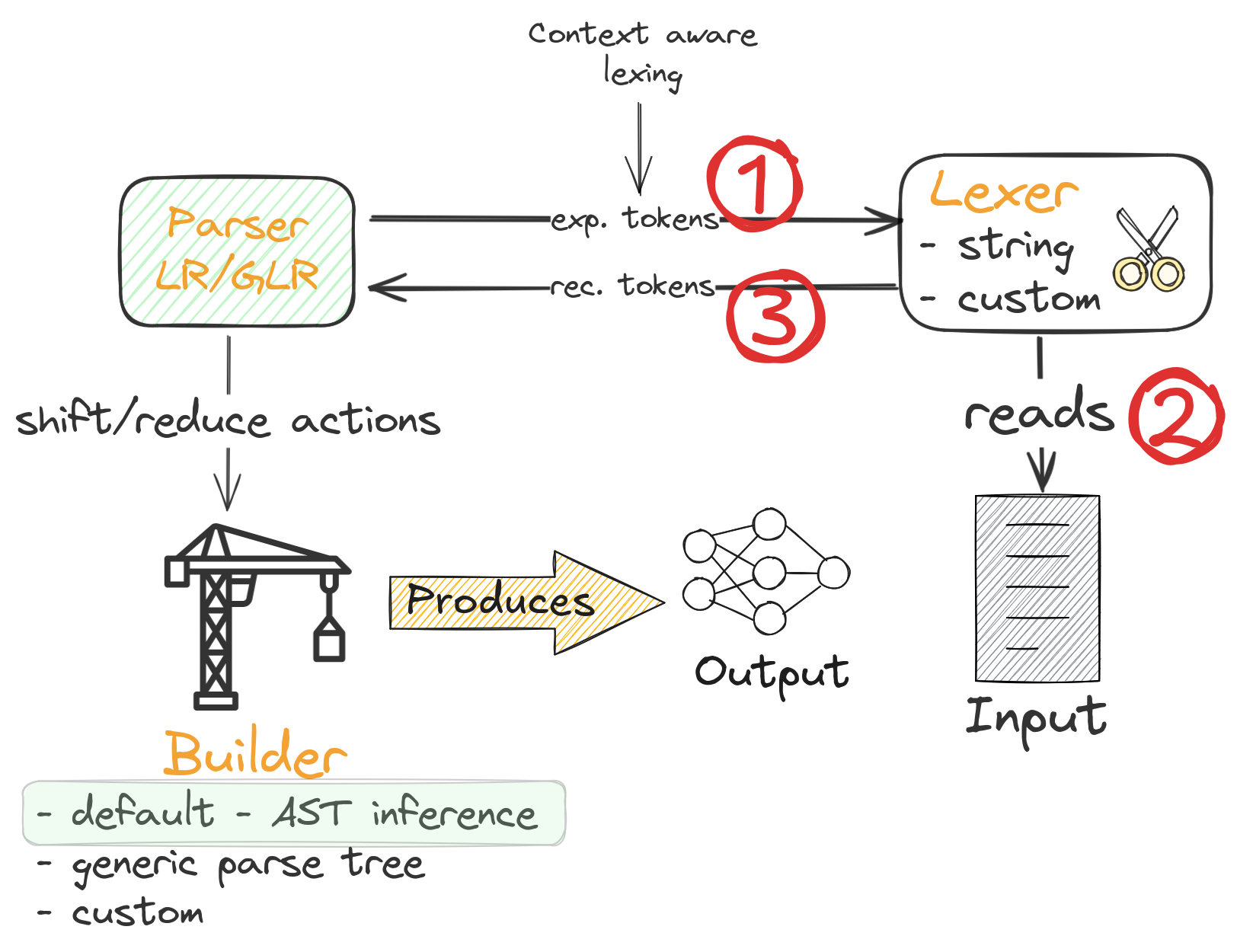
1.9. Parsing process overview
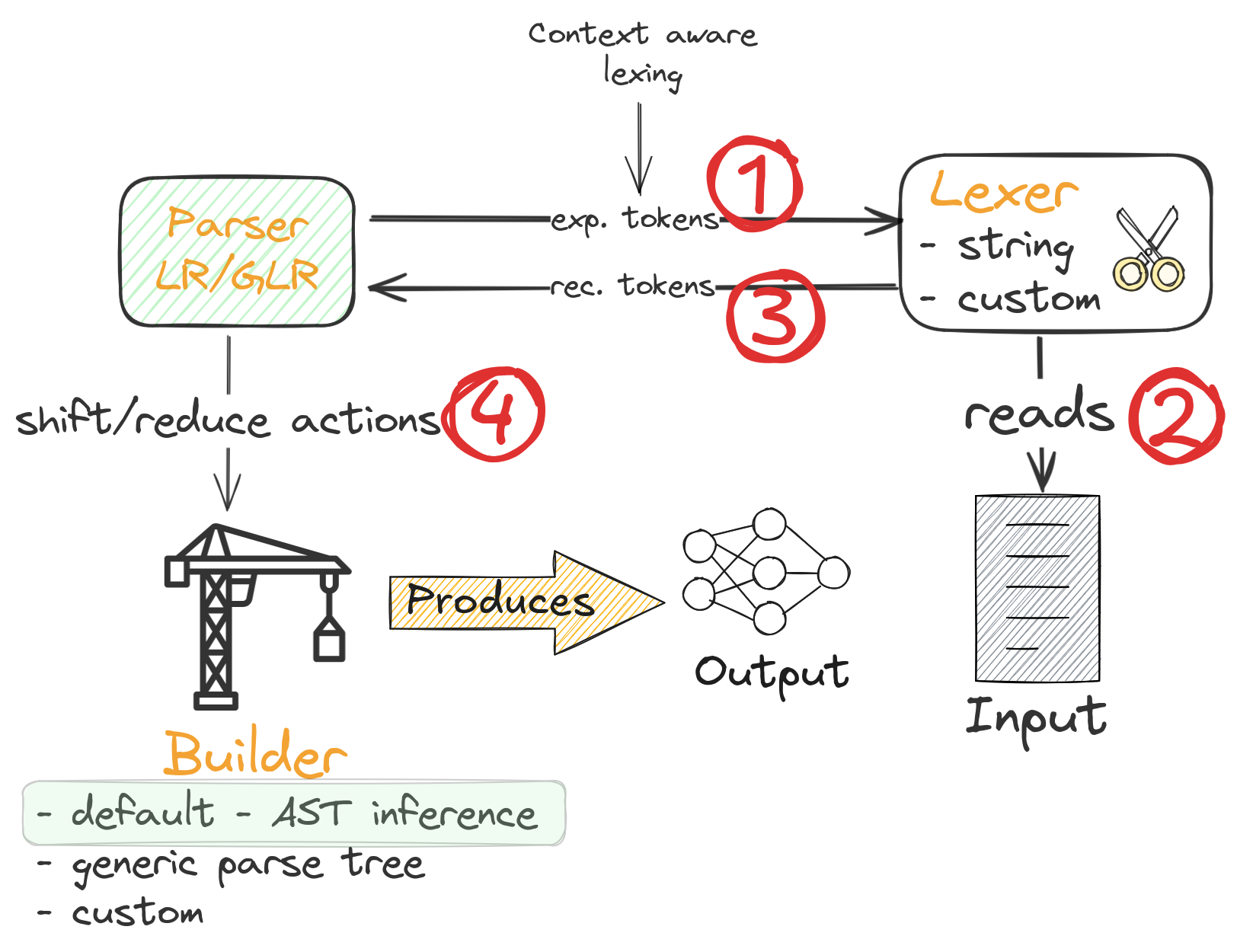
1.10. Parsing process overview
2. Live demo - arithmetic expressions
2.1. Demo repository
- GitHub repo
- Each step in this demo is a separate commit in the Git repo
- Use diff to see what changed in each step
- These slides are linked to relevant commits/steps - look for
step xin titles.
- Prerequisite - Rust installed
2.2. Initial project
2.2.1. Create initial Rust project (step 1)
cargo new --bin arithmetic
Project layout is:
.
└── arithmetic
├── Cargo.toml
└── src
└── main.rs
2.2.2. Create expression grammar (step 2)
File src/arithmetic.rustemo
E: E '+' E
| E '*' E
| '(' E ')'
| Number
;
terminals
Number: /\d+/;
Add: '+';
Mul: '*';
POpen: '(';
PClose: ')';
2.2.3. Install Rustemo compiler
cargo install rustemo-compiler
After the installation completes the compiler (rcomp CLI tool) is available.
2.2.4. Try to compile the grammar
cd arithmetic/src/
rcomp arithmetic.rustemo
Generating parser for grammar "arithmetic.rustemo"
Terminals: 6
Non-terminals: 1
Productions: 4
States: 10
CONFLICTS:
In State 8:E
1: E: E Add E . {STOP, Add, Mul, PClose}
1: E: E . Add E {STOP, Add, Mul, PClose}
2: E: E . Mul E {STOP, Add, Mul, PClose}
When I saw E and see token Add ahead I can't decide should I shift or reduce by production:
E: E Add E
In State 8:E
1: E: E Add E . {STOP, Add, Mul, PClose}
1: E: E . Add E {STOP, Add, Mul, PClose}
2: E: E . Mul E {STOP, Add, Mul, PClose}
When I saw E and see token Mul ahead I can't decide should I shift or reduce by production:
E: E Add E
...
4 conflict(s). 4 Shift/Reduce and 0 Reduce/Reduce.
Error: Grammar is not deterministic. There are conflicts.
Parser(s) not generated.
This grammar is ambiguous!
2.2.5. We can also visualize DFA for this grammar (step 3)
cd arithmetic/src
rcomp --dot arithmetic.rustemo
dot -Tpng -O arithmetic.dot
We get a PNG file with the DFA.
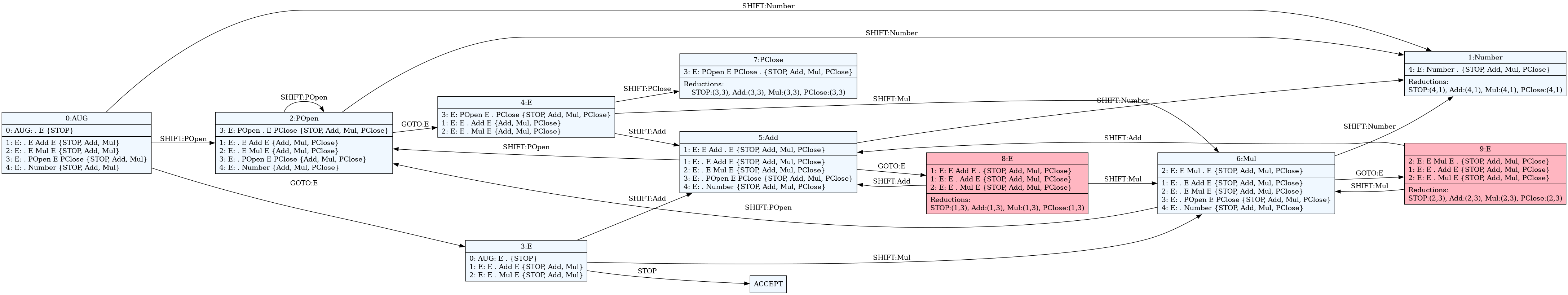
States colored red have conflicts.
2.3. Ambiguous grammars
2.3.1. What does it mean for a grammar to be ambiguous?
1 + 2 * 3 + 4
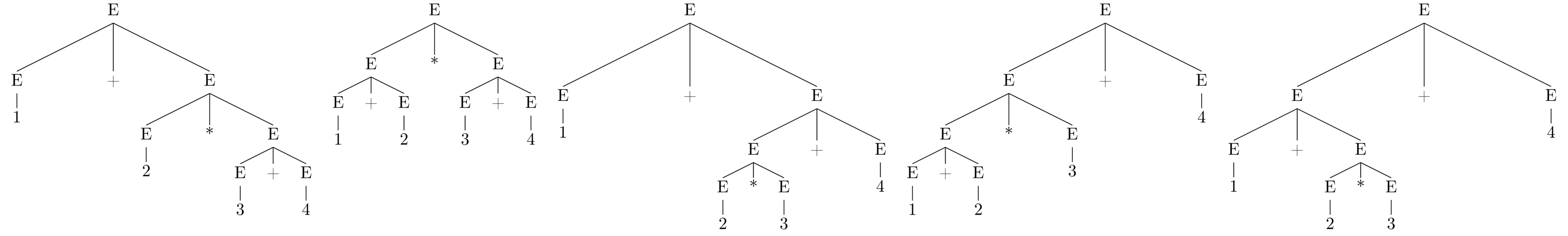
- The number of possible interpretation rise quickly with the addition of new operations.
- 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, … - Catalan numbers
2.3.2. What does it mean for a grammar to be ambiguous?
1 + 2 * 3 + 4
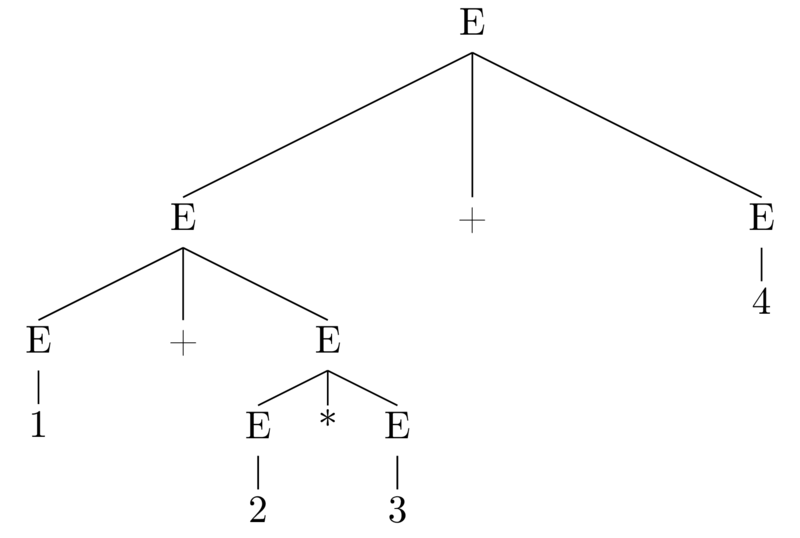
While the grammar is ambiguous, the language is not!
2.3.3. How to disambiguate?
A classic approach - grammar rework by introducing intermediate rules:
AddExpr: MulExpr AddExprRest*;
AddExprRest: Add MulExpr;
MulExpr: AtomExpr MulExprRest*;
MulExprRest: Mul AtomExpr;
AtomExpr: Number | '(' AddExpr ')';
terminals
Number: /\d+/;
Add: '+';
Mul: '*';
POpen: '(';
PClose: ')';
We stay in the CFG realm, but this quickly leads to unmaintainable grammar + produced trees are not what the user expects.
2.4. Using GLR
2.4.1. Ok, lets try GLR (step 4)
- GLR - Generalized LR - can accept any CFG, even ambiguous.
- Explores and returns all possible interpretations efficienly (polinomial time/space).
We’ll just let the grammar be without any disambiguation.
E: E '+' E
| E '*' E
| '(' E ')'
| Number
;
terminals
Number: /\d+/;
Add: '+';
Mul: '*';
POpen: '(';
PClose: ')';
Now, lets compile the grammar to a GLR parser.
rcomp --parser-algo glr arithmetic.rustemo
Generating parser for grammar "arithmetic.rustemo" Terminals: 6 Non-terminals: 1 Productions: 4 States: 10 Writing actions file "arithmetic_actions.rs" Writing parser file "arithmetic.rs"
2.4.2. Add required dependencies (step 5)
Generated parser depends on rustemo library. It is a runtime part of the Rustemo.
cargo add rustemo
Updating crates.io index
Adding rustemo v0.6.0 to dependencies
Features:
+ glr
Updating crates.io index
Generated code also uses regex, once_cell and colored libraries, so lets add those.
cargo add regex --no-default-features --features std,unicode-perl
cargo add once_cell colored
Now, your Cargo.toml should look like this:
[package]
name = "arithmetic"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
[dependencies]
colored = "2.1.0"
once_cell = "1.20.1"
regex = { version = "1.11.0", default-features = false, features = ["std", "unicode-perl"] }
rustemo = "0.6.1"
2.4.3. Update main.rs
Read expression from stdin.
fn main() {
let mut expression = String::new();
// Read the line from the input
println!("Expression:");
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut expression)
.expect("Failed to read line.");
}
2.4.4. Update main.rs
Import generated parser modules and the parser type.
use rustemo::Parser;
use std::io;
// Use the generated parser
use crate::arithmetic::ArithmeticParser;
// Include generated modules
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic;
#[allow(unused)]
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic_actions;
fn main() {
let mut expression = String::new();
// Read the line from the input
println!("Expression:");
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut expression)
.expect("Failed to read line.");
}
2.4.5. Update main.rs (step 6)
Parse the input and process the forest.
use rustemo::Parser;
use std::io;
// Use the generated parser
use crate::arithmetic::ArithmeticParser;
// Include generated modules
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic;
#[allow(unused)]
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic_actions;
fn main() {
let mut expression = String::new();
// Read the line from the input
println!("Expression:");
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut expression)
.expect("Failed to read line.");
// Parse the line and get all results.
let forest = ArithmeticParser::new().parse(&expression).unwrap();
println!("Number of interpretations = {}", forest.solutions());
for (tree_idx, tree) in forest.iter().enumerate() {
println!("**** TREE {tree_idx}");
println!("{tree:#?}");
}
}
Run with:
cargo run
Expression:
2 + 3 * 5
Number of interpretations = 2
**** TREE 0
[
[
[
"2",
],
"+",
[
"3",
],
],
"*",
[
"5",
],
]
**** TREE 1
[
[
"2",
...
2.4.6. Improve default actions
- The builder can be changed. See builders section in the Rustemo book for more info.
- The default builder calls actions to create AST nodes where the types are auto-inferred from the grammar.
- Actions are generated Rust functions.
2.4.7. Improve default actions
File arithmetic_actions.rs
<snip>
pub type Number = String;
pub fn number(_ctx: &Ctx, token: Token) -> Number {
token.value.into()
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub struct EC1 {
pub e_1: Box<E>,
pub e_3: Box<E>,
}
<snip>
pub fn e_c1(_ctx: &Ctx, e_1: E, e_3: E) -> E {
E::C1(EC1 {
e_1: Box::new(e_1),
e_3: Box::new(e_3),
})
}
pub fn e_number(_ctx: &Ctx, number: Number) -> E {
E::Number(number)
}
This just creates an AST. But, we would like actions to perform actual calculation. Let’s do that!
2.4.8. Improve actions - add nice production names
E: E '+' E {Add}
| E '*' E {Mul}
| '(' E ')' {Paren}
| Number {Num}
;
terminals
Number: /\d+/;
Add: '+';
Mul: '*';
POpen: '(';
PClose: ')';
2.4.9. Improve actions - add assignments
E: left=E '+' right=E {Add}
| left=E '*' right=E {Mul}
| '(' E ')' {Paren}
| Number {Num}
;
terminals
Number: /\d+/;
Add: '+';
Mul: '*';
POpen: '(';
PClose: ')';
2.4.10. Improve actions - regenerate (step 7)
- Actions are regenerated on each
rcomprun. - Old content is preserved as we are able to manually tune actions and types.
In this case we don’t have manual changes so we just delete
arithmentic_actions.rsand runrcompagain.rm arithmetic_actions.rs rcomp --parser-algo glr arithmentic.rustemo
2.4.11. Improve actions - improved
And, now our actions are more readable.
pub type Token<'i> = RustemoToken<'i, Input, TokenKind>;
pub type Number = String;
pub fn number(_ctx: &Ctx, token: Token) -> Number {
token.value.into()
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub struct Add {
pub left: Box<E>,
pub right: Box<E>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub struct Mul {
pub left: Box<E>,
pub right: Box<E>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub enum E {
Add(Add),
Mul(Mul),
Paren(Box<E>),
Num(Number),
}
2.4.12. Improve actions - improved
And, now our actions are more readable.
pub fn e_add(_ctx: &Ctx, left: E, right: E) -> E {
E::Add(Add {
left: Box::new(left),
right: Box::new(right),
})
}
pub fn e_mul(_ctx: &Ctx, left: E, right: E) -> E {
E::Mul(Mul {
left: Box::new(left),
right: Box::new(right),
})
}
pub fn e_paren(_ctx: &Ctx, e: E) -> E {
E::Paren(Box::new(e))
}
pub fn e_num(_ctx: &Ctx, number: Number) -> E {
E::Num(number)
}
2.4.13. Improve actions - calculate
We can now manually tune our actions to do calculations during the build. We don’t want to build the tree, we want to get the result of the calculation.
First, we change this:
pub type Number = String;
pub fn number(_ctx: &Ctx, token: Token) -> Number {
token.value.into()
}
Into this:
pub type Number = i32;
pub fn number(_ctx: &Ctx, token: Token) -> Number {
token.value.parse().unwrap()
}
to convert numbers from strings to integers.
2.4.14. Improve actions - calculate
We replace all these types.
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub struct Add {
pub left: Box<E>,
pub right: Box<E>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub struct Mul {
pub left: Box<E>,
pub right: Box<E>,
}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub enum E {
Add(Add),
Mul(Mul),
Paren(Box<E>),
Num(Number),
}
With just:
pub type E = i32;
2.4.15. Improve actions - calculate
Now, we replace actions bodies with a proper calculations.
We replace this:
pub fn e_add(_ctx: &Ctx, left: E, right: E) -> E {
E::Add(Add {
left: Box::new(left),
right: Box::new(right),
})
}
pub fn e_mul(_ctx: &Ctx, left: E, right: E) -> E {
E::Mul(Mul {
left: Box::new(left),
right: Box::new(right),
})
}
pub fn e_paren(_ctx: &Ctx, e: E) -> E {
E::Paren(Box::new(e))
}
pub fn e_num(_ctx: &Ctx, number: Number) -> E {
E::Num(number)
}
2.4.16. Improve actions - calculate (step 8)
Now, we replace actions bodies with a proper calculations.
With this:
pub fn e_add(_ctx: &Ctx, left: E, right: E) -> E {
left + right
}
pub fn e_mul(_ctx: &Ctx, left: E, right: E) -> E {
left * right
}
pub fn e_paren(_ctx: &Ctx, e: E) -> E {
e
}
pub fn e_num(_ctx: &Ctx, number: Number) -> E {
number
}
2.4.17. Improve actions - run
Run it again:
cargo run
- Nothing changed! Why?
- When using GLR, trees are not converted by builders automatically as it would impose a big overhead.
- We must call builder explicitly over trees extracted from the forest.
2.4.18. GLR - calculate over all trees
Change our main.rs to build all trees from the forest using our new calculation
actions.
2.4.19. GLR - calculate over all trees
Change from this:
use rustemo::Parser;
use std::io;
// Use the generated parser
use crate::arithmetic::ArithmeticParser;
// Include generated modules
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic;
#[allow(unused)]
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic_actions;
fn main() {
let mut expression = String::new();
// Read the line from the input
println!("Expression:");
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut expression)
.expect("Failed to read line.");
// Parse the line and get all results.
let forest = ArithmeticParser::new().parse(&expression).unwrap();
println!("Number of interpretations = {}", forest.solutions());
for (tree_idx, tree) in forest.iter().enumerate() {
println!("**** TREE {tree_idx}");
println!("{tree:#?}");
}
}
2.4.20. GLR - calculate over all trees
To this:
use rustemo::Parser;
use std::io;
// Use the generated parser and builder
use crate::arithmetic::{ArithmeticParser, DefaultBuilder};
// Include generated modules
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic;
#[allow(unused)]
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic_actions;
fn main() {
let mut expression = String::new();
// Read the line from the input
println!("Expression:");
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut expression)
.expect("Failed to read line.");
// Parse the line and get all results.
let forest = ArithmeticParser::new().parse(&expression).unwrap();
println!("Number of interpretations = {}", forest.solutions());
// Evaluate each tree from the forest
let results = forest
.into_iter()
.map(|tree| {
let mut builder = DefaultBuilder::new();
tree.build(&mut builder)
})
.collect::<Vec<_>>();
println!("{results:?}");
}
2.4.21. GLR - calculate over all trees (step 9)
To this:
// Parse the line and get all results.
let forest = ArithmeticParser::new().parse(&expression).unwrap();
println!("Number of interpretations = {}", forest.solutions());
// Evaluate each tree from the forest
let results = forest
.into_iter()
.map(|tree| {
let mut builder = DefaultBuilder::new();
tree.build(&mut builder)
})
.collect::<Vec<_>>();
println!("{results:?}");
2.5. Declarative disambiguation
2.5.1. Rustemo - declarative disambiguation
But, this language is not ambiguous. We have priorities and associativities. Let’s disambiguate by using Rustemo declarative disambiguation so we can use LR instead of GLR.
E: left=E '+' right=E {Add}
| left=E '*' right=E {Mul}
| '(' E ')' {Paren}
| Number {Num}
;
terminals
Number: /\d+/;
Add: '+';
Mul: '*';
POpen: '(';
PClose: ')';
2.5.2. Rustemo - declarative disambiguation
E: left=E '+' right=E {Add, 1, left}
| left=E '*' right=E {Mul, 2, left}
| '(' E ')' {Paren}
| Number {Num}
;
terminals
Number: /\d+/;
Add: '+';
Mul: '*';
POpen: '(';
PClose: ')';
2.5.3. Regenerate the parser
Now, we can use LR.
rcomp arithmetic.rustemo
Generating parser for grammar "arithmetic.rustemo" Terminals: 6 Non-terminals: 1 Productions: 4 States: 10 Writing actions file "arithmetic_actions.rs" Writing parser file "arithmetic.rs"
2.5.4. Fix main.rs for LR
Now, we don’t get a forest from the LR parser but the result of the default builder evaluation. Let’s fix that.
2.5.5. Fix main.rs for LR
We change main.rs from this:
use rustemo::Parser;
use std::io;
// Use the generated parser and builder
use crate::arithmetic::{ArithmeticParser, DefaultBuilder};
// Include generated modules
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic;
#[allow(unused)]
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic_actions;
fn main() {
let mut expression = String::new();
// Read the line from the input
println!("Expression:");
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut expression)
.expect("Failed to read line.");
// Parse the line and get all results.
let forest = ArithmeticParser::new().parse(&expression).unwrap();
println!("Number of interpretations = {}", forest.solutions());
// Evaluate each tree from the forest
let results = forest
.into_iter()
.map(|tree| {
let mut builder = DefaultBuilder::new();
tree.build(&mut builder)
})
.collect::<Vec<_>>();
println!("{results:?}");
}
2.5.6. Fix main.rs for LR (step 10)
To this:
use rustemo::Parser;
use std::io;
// Use the generated parser
use crate::arithmetic::ArithmeticParser;
// Include generated modules
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic;
#[allow(unused)]
#[rustfmt::skip]
mod arithmetic_actions;
fn main() {
let mut expression = String::new();
// Read the line from the input
println!("Expression:");
io::stdin()
.read_line(&mut expression)
.expect("Failed to read line.");
// Parse the line and get the result.
let result = ArithmeticParser::new().parse(&expression).unwrap();
println!("Result = {result}");
}
3. Conclusion
- Learn more
- Possible further directions
- Grammars modularization, rule inheritance/macros etc.
- Additional disambiguation filters (static & dynamic)
- Error recovery
- Incremental parsing
- Tooling for working with Rustemo grammars (e.g. LSP server, plugins for popular editors).
- Rustemo is FLOSS and open for contributions!
Thanks!
Q&A

